What’s new and important in VMware Virtual SAN 6.2
VMware recently released a new version of their vSan product, version 6.2. It is a important releases in the battlefield of the (software defined) storage wars. Here's what's new and important in VMware Virtual SAN 6.2.
Data Efficiency (Deduplication and Compression)
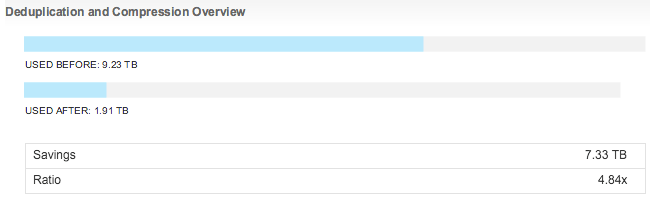
Dedupe and compression happens during de-staging from the caching tier to the capacity tier. You enable “space efficiency” on a cluster level and deduplication happens on a per disk group basis. Bigger disk groups will result in a higher deduplication ratio. After the blocks are deduplicated, then they are compressed. A significant saving already, but combined with deduplication, the results achieved can be up to 7x space reduction, of course fully dependent on the workload and type of VMs.
RAID-5/RAID-6 – Erasure Coding
Sometimes RAID 5 and RAID 6 over the network is also referred as erasure coding. In this case, RAID-5 requires 4 hosts at a minimum as it uses a 3+1 logic. With 4 hosts, 1 can fail without data loss. This results in a significant reduction of required disk capacity. Normally a 20GB disk would require 40GB of disk capacity, but in the case of RAID-5 over the network, the requirement is only ~27GB. There is another option if higher availability is desired. Learn more about the use of Erasure Coding in Virtual SAN 6.2.
Quality of Service (QoS)
This enables per VMDK IOP Limits. They can be deployed by Storage Policy-Based Management (SPBM), tying them to existing policy frameworks. Service providers can use this to create differentiated service offerings using the same cluster/pool of storage. Customers wanting to mix diverse workloads will be interested in being able to keep workloads from impacting each other.
Software Checksum
Software Checksum will enable customers to detect the corruptions that could be caused by hardware/software components including memory, drives, etc. during the read or write operations. In the case of drives, there are two basic kinds of corruption. The first is “latent sector errors”, which are typically the result of a physical disk drive malfunction. The other type is silent corruption, which can happen without warning (These are typically called silent data corruption). Undetected or completely silent errors could lead to lost or inaccurate data and significant downtime. There is no effective means of detection without end-to-end integrity checking.
IPV6
Virtual SAN can now support IPv4-only, IPv6-only, and also IPv4/IPv6-both enabled. This addresses requirements for customers moving to IPv6 and, additionally, supports mixed mode for migrations.
Performance Monitoring Service
Performance Monitoring Service allows customers to be able to monitor existing workloads from the vCenter. Customers needing access to tactical performance information will not need to go to vRO. Performance monitor includes macro level views (Cluster latency, throughput, IOPS) as well as granular views (per disk, cache hit ratios, per disk group stats) without needing to leave vCenter. The performance monitor allows aggregation of states across the cluster into a “quick view” to see what load and latency look like as well as share that information externally directly to 3rd party monitoring solutions by API.The Performance monitoring service runs on a distributed database that is stored directly on Virtual SAN.
Check out the Technical White paper for ALL the details.
Source: https://blogs.vmware.com/virtualblocks/2016/02/10/whats-new-vmware-virtual-san-6-2/